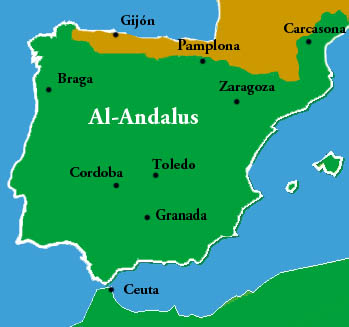
West Asia in History III
COURSE OUTCOMES
1. Historically evaluate the socio-political and economic transformation of Egypt, Turkey and the Levantine countries
2. Critically analyses the development of modern constitutionalism in Egypt and Iran
3. Understand the consequence of wars and its effect on West Asia and emergence of Arab nationalism
4. Examine the concept of Arab Nationalism, Mandate system and their impact on the people and the region in general
5. Critically evaluate the
independence of Lebanon, Syria and republic of Turkey

Functional Arabic-I
COURSE OUTCOMES
1. Introduce origin, influence and features of the Arabic language.
2. Familiarise with Arabic letters, words and simple sentences.
3. Get acquainted with simple grammar and laws of structuring sentences.
4. Practice formulating simple sentences.
5. Impart ability to read, write and construct simple sentencesMODULES I Introduction to
the Arabic Language, its features and influences in the contemporary world.
II Arabic
Letters, Sound system III Script,
Orthographic signs. IV Basic patterns
of structure. V Introducing
Arab Media, Cinema and Prominent Writers. VI Vocabulary of Arabic Language - Practical Sessions on
the exercise in the prescribed Text Books.

STATE AND POLITICS IN WEST ASIA
COURSE OUTCOMES
1. Understanding the evolution of West Asian Society and Politics.
2. Critically locating the genealogy of modern state making in the Arab World, its conflict with the tradition and implications of modernity therein.
3. Examining the Arab world’s intertwined history, exchange of ideas and politics with Europe.
4. To guide students to have a theoretical perspective on the nature of political systems and their crisis in the present.
5. Evaluate and look at the concept of globalization’s effect on the nature of politics and state. Also look at the critique of state power and violence within the intellectual cross currents of the region
MODULES
I Brief History of State formation - Islam as a Factor of Political Legitimacy- Islam and Nation-State –Origin of the Arabo- Islamic State.
II State Formation in the Modern Era – The European encroachment- A colonial mode of Production.
III Post-Colonial State - Arab Nationalism – The Pan- Arabist Ideology-Post - Liberalization Political Changes - Religious and ethnic diversities.
IV Approaches to the Understanding of State -Neo-Patriarchy -Arab Marxism - Rentierism - Post-Secularism.
V Typology of Governments - Nature of State and State Apparatuses – Political Reform and Democratization-Islamic Movements.
VI State in Transition- The role of tradition - The impact of the West Globalization.

WEST ASIA IN INTERNATIONAL POLITICS
The course enables the students to evaluate the dynamics of International Politics in West Asia. To enable the students to have an understanding of the political developments of West Asia in the context of Global Political events.

Islamic Philosophy and Theology – Sects and Trends
Understand basic historical overview of the trends and sects in Islam
understand the various dimensions of Islamic theology and philosophy
Analyse the theological and philosophical debates of different sects in Islam
Classify the contributions of great philosophers and theologians by analyzing how different Muslim thinkers approached the scholastic debates
Evaluate the contributions of Indian Islamic philosophers in comparison with prominent Mulim thinkers.

Arab-Muslim Historiography
Understand the contributions of Arab Muslim historiography
Identify the features of Arab Muslim historiography
Evaluate the works of medieval Indian historians and Kerala historians
Learn to use the conceptual tools to analyse the authenticity of the historical writings of the early period.
Explore the manuscript tradition of the texts and their importance as sources for the history of the period
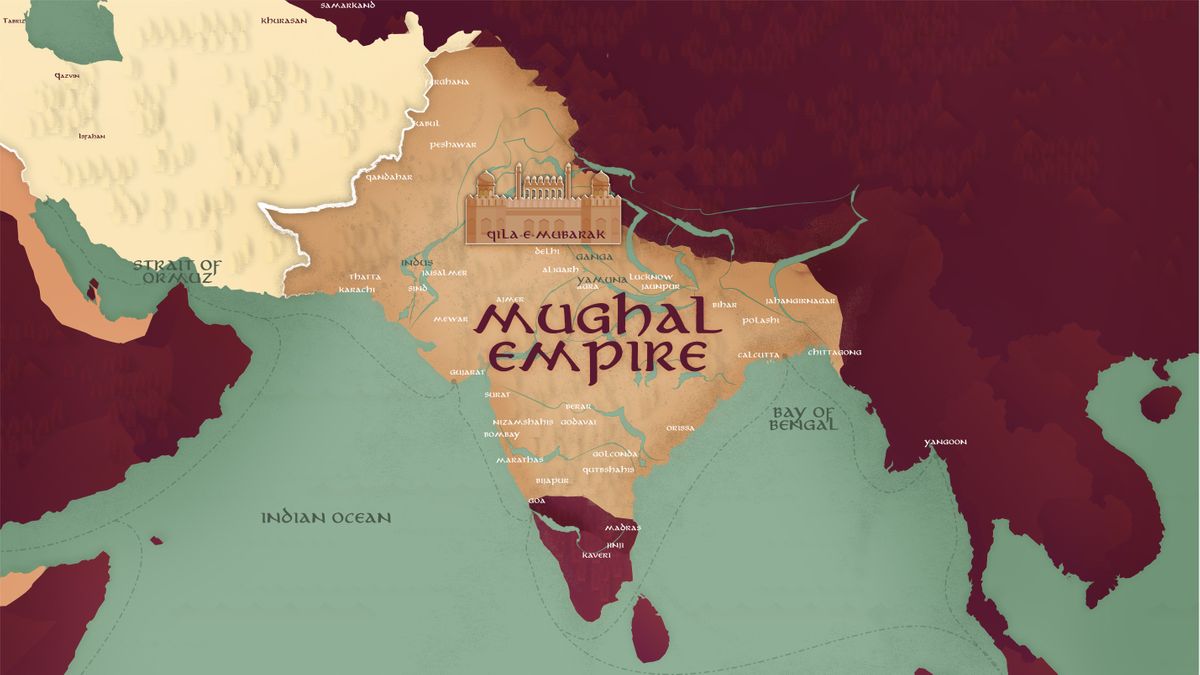
ISLAM IN INDIA – PART II (Later Medieval India)
The course gives a comprehensive and analytical study on the administration and society under the Mughals. It particularly makes an emphasis on the religious policies adopted under Akbar and Aurangazeb. The evolution of Indo- Islamic Architecture and the development of socio-economic changes during the period are covered in the course.
Course Outcomes
1. Explain the glorious heritage and history of later medieval India
2. Analyze the policies of Mughal rulers and Suri rulers
3. Understand the features of Muslim administrative systems
4. Estimate the intellectual progress and the development of art and architecture under
Mughals
5. Discuss the religious and political policies of Mughal rulers

ISLAM IN INDIA – PART I (Early Medieval India)
The course specifies the background related to the arrival and spread of Islam to India. It emphasizes the emergence of various movements and organizations during the period. The course starting from the period of Indo-Arab trade links before the rise of Islam, passes through the periods of the Ghaznavids ,Ghoris and the Delhi Sultanate, and ends with the various reasons for the decline of the Sultanate.
Course Outcomes
1. Outline the Indo-Arab trade links before the rise of Islam
2. Outline the Turkish conquest of Indian Subcontinent
3. Assess the reforms and policies of the Delhi Sultanate
4 .Analyze the impact of Bhakthi and Sufi Movements
5. Evaluate the art and architecture and the development of historiography under the Delhi
Sultanate
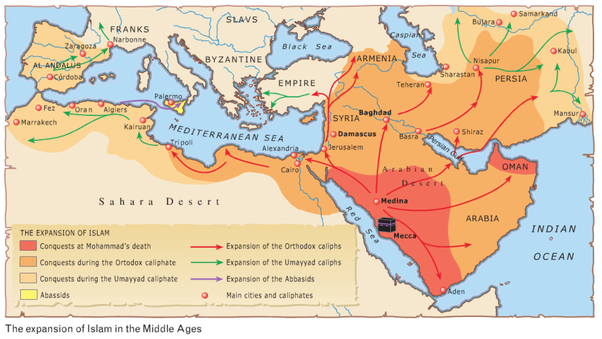
UMAYYADS AND THE ABBASIDS
The course covers the Umayyad and Abbasid dynasties and their powerful rulers. The cultural, administrative and intellectual contributions are depicted with specific remarks under Umayyads. In an in-depth study regarding the greatest glory of Bagdad city under Abbasids in Art, Science, Literature, Theology, Jurisprudence and Architecture is included.
Course Outcomes
1. Understand the great Muslims civilizations flourished from the 7th to 10th centuries
2.. Analyze the Muslims expeditions in Indian Sub Continent, North Africa, and South West
Europe with a clear perspective
3.. Evaluate the intellectual progress under the Umayyads and Abbasids
4.. Compare the administrative models and literary developments under the Abbasids and the
Umayyads
5.. Evaluate the four schools of Islamic Jurisprudence

Arab-Israeli Conflict
Course Outcomes
1. Understanding the nature and the history of conflict.
2. Critically locating the genealogy of modern state making and violence, the relationship between the colonizer and the colonized.
3. Studying the Palestinian Dispossession and the question of ‘Rights’.
4. Engaging with critical methods and new materials to understand the everyday life of the Palestinian people entangled in the colony.
5. Understanding the contemporary relevance of Arab-Israeli conflict in the world’s engagement with the region.

LIFE AND TIMES OF THE HOLY PROPHET
The course makes awareness among students in the geography of
Arabia, its people, tribal life and culture, religious beliefs and social
system prevailed in the pre- Islamic days. It also opens light on the early
career of the Prophet, the days of the Prophethood, troubled days in Makkah and
Hijrah to Madina. In the Madinite life of the Prophet, the course describes in
detail the defensive wars he led, the administrative set up he laid on, the
religious teachings he imparted and the ideal society he framed.
Course Outcomes
1. Identify the geographical features and the Semitic races of Arabian Peninsula
2. Understand the culture and the literal development of pre-Islamic Arabia
3. Analyze the life of Prophet Muhammed as a prophet and statesman
4. Find the religious customs and traditions of Muslims in Arabia
5. Assess the ideological foundations of Islam in comparison with the modern idelogies

ISH - CC-423: ISLAM IN AFRICA - FATIMIDS TO THE MAMLUKES
Course Learning Outcomes
Understand the major factors for the rise of Islam in Africa.
Analyse the political and social development under the Mamlukes.
Compare and contrast between the Fatimids and the Abbasids with regards to their achievements in science and learning.
Critically examine the Crusades and the Muslim reaction on it.
Assess the intellectual contribution of the Mamluk period.
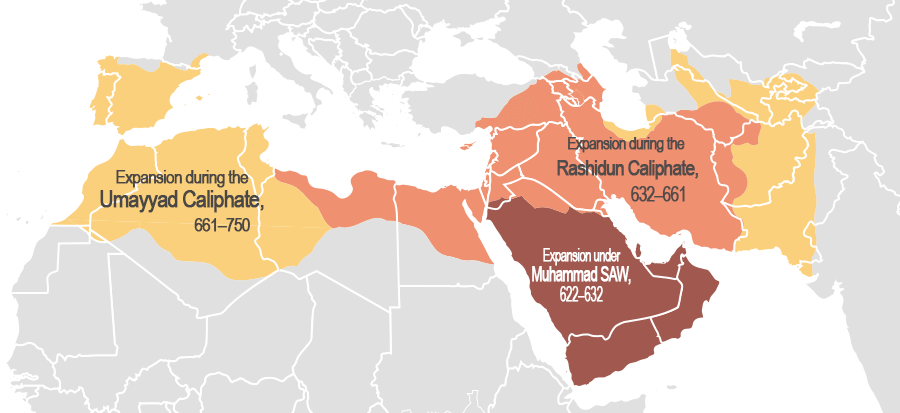
ADVENT OF THE ISLAMIC STATE-PIOUS CAIPHATE
Course Learning Outcomes
Assess the personality of the pious caliphs.
Explain the democratic elements of the pious Caliphs.
Critically examine the circumstances which led to the assassination of Khalifah Uthman.
Illustrate the administrative system of the pious Caliphs.
Examine the causes and nature of the Riddah wars during the caliphate of Abu Bakr.
Analyse factors responsible for the breakdown of the pious Caliphs.

ISH-E-434: Reform Movements in Islam
This course is offered for III-semester MA Islamic History students of the Department of Islamic Studies.
After completion of the modules, the student should be able to:
- Compare and contrast the views of different religious reformers
- Understand the terms Taqlid and Tajdid and realize the qualities of a Mujaddid.
- Assess how far the remedies advocated by different religious scholars like Muhammad ibn Abdul Wahhab, Abul Ala Maududi, Umar Ibn Abdul Aziz, Imam Ahmed Ibn Hambal, Ibn Taimiyah, to revitalizing Islam in India.
- Realize the role of religious movements like Muwahhidun movement, Sanussiyah movement, Pan-Islamism, Ikhwanul Muslimun, Jamat-e-Islami, Salafi Movement, etc.

Historical Method and Historiography
Course Outcomes
1. Understand the fundamental tenets of history-nature, scope, definition, and relation to
Other social sciences.
2. Understand the fundamental principles to be observed in history writing
3. Analyze the contribution of historians of the ancient and medieval period together with those of the modern period.
4. Discover the various sources and their significance in historical writing and research
5. Understand the various no-documentary sources and their collection and use
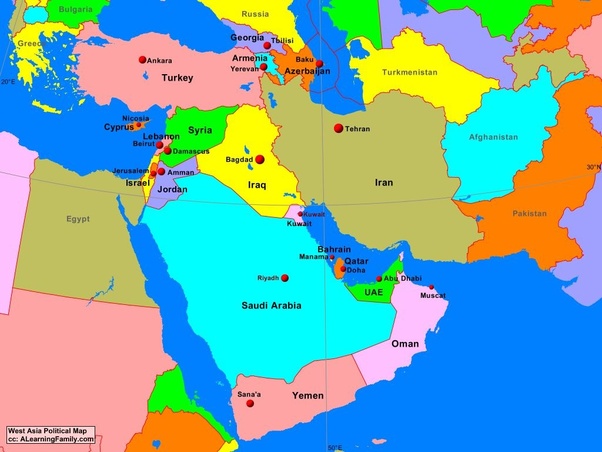
Understanding the Region: Society and Culture
Course Outcomes
1. Acquire a general understanding of the West Asian region through critical cartographic practices.
2. Understand the Evolution of the region in spatial-temporal sense from the beginning of civilization as it passed from ancient, religious state to secular state and beyond.
3. Critically study region’s historical, cultural and political formations as it passed from one epoch to another.
4. Get acquainted with the region’s intertwined history of religions, culture and life forms.
5. Critically look at the concept of Political Islam in the context of modernity.
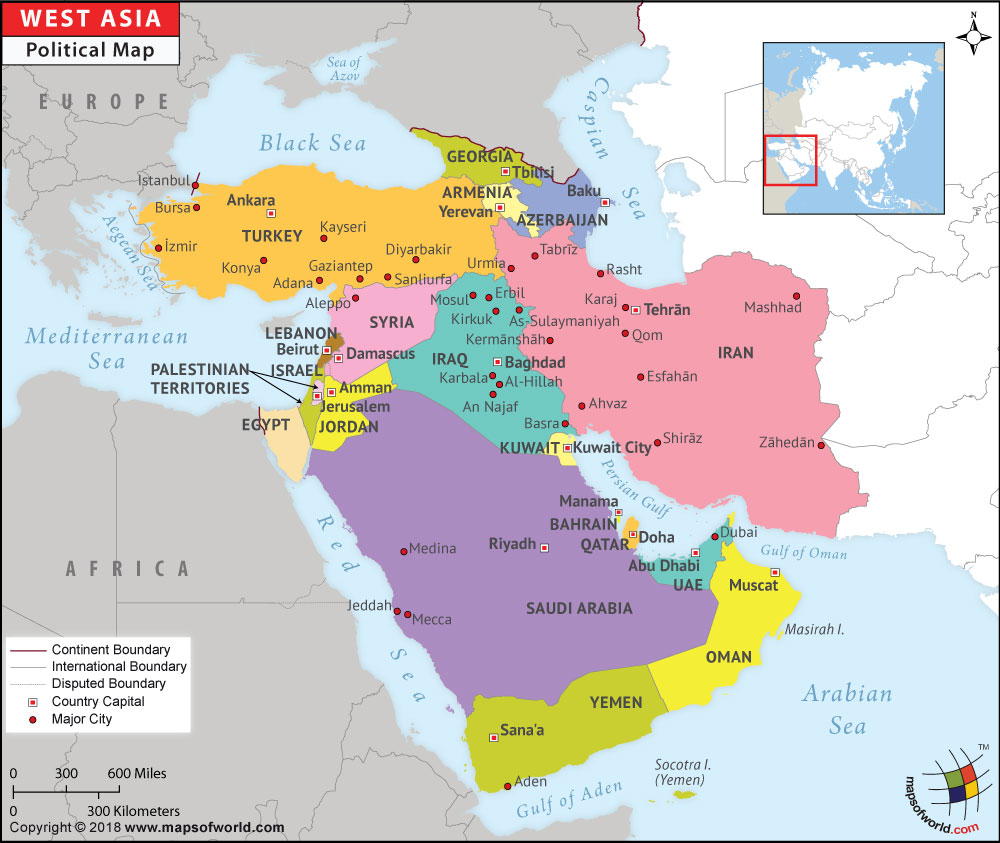
West Asia in History II
To familiarize the students
the History and Culture of West Asia. A wide understanding about the history of
the region is essential to have an idea about the various other aspects of it.

Islam and Orientalism
the course enables students to define and evaluate the concept of orientalim as it has been used historically. This will help to identify and evaluate the issues in modern scholarly debates about meaning and connotations of the term.
Ever since the conflict between the Christendom and Islamic world started especially in the context of crusades the otherness has come into being.The trend has expanded greatly during the period of European explorations, colonisation and imperialism. These European explorations in the Islamic world produced a plethora of literature. Those who studied and wrote on this topics became known as as orientalists.
The scholarly study
and conventional understanding of Islam and the West Asian region was, and has
been, dramatically challenged by the appearance of Edward Said’s seminal work, Orientalism. Ever since its
publication, the discipline of Middle Eastern Studies has debated the validity
of its critique, applied it to many case studies, challenged it in return, and
continues to ponder its implications for the future study of the area. This
module introduces students to the origins of these debates within a general
context of scholarly developments in the field of Islamic and West Asian Studies
in the Post Industrial world. It then
follows the vicissitudes of the debate to its present phase and attempts to
assess its future influence on the field